visibility measurement to test the effectiveness of a wiper system
(version Française ICI)
A wiper system on a modern vehicle is composed of several modules (motors, windshield with surface is treatment , arms, rubber , rain sensor , brightness sensor , automatic trigger software for automatic wiping mode, ... ) .
If you consider six elements (parts of the wiper system) that can each take 10 references (or adjustments/tuning or location) then you get ten power six possibilities , that is to say 1 million different wiper systems from the same organs.
No doubt that this combinatorial is hard to test in an exhaustive way ...
Moreover, since wiping goal is to restore our vision , it is important to note that the disruption of visibility due to rain are more or less felt depending on the characteristics of the road scene : light level , direction of lighting, size of raindrops , rainfall, vehicle speed, road markings ... Again, life situations are very numerous, so that the crossing (characteristic of wiping ) x ( life situation ) gives rise to a very large number of cases ( more than ten power ten solutions) . The test of this combination is complex as the road is an open area where light rain ... are not controlled , but "suffered".
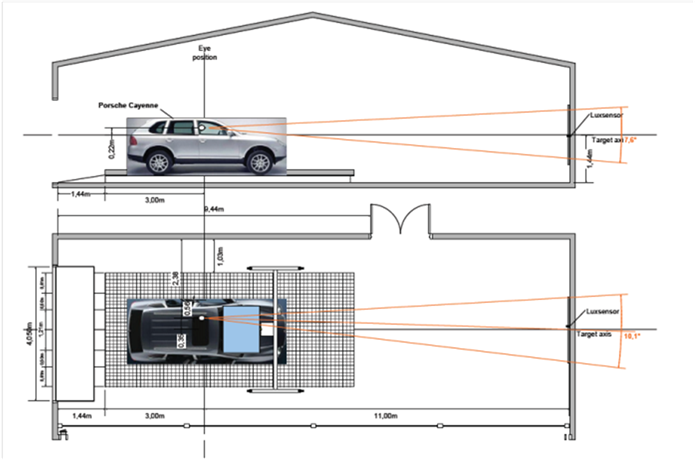
To proceed to industrial test of a wiper system, it is necessary to control the disturbance of visibility due to rain ( artificial rain machine producing representative and reproducible artificial rain) , and have a test bench on which to implement design plans ( orthogonal and fractional ) to model the impact of setting parameters of the wiper system on visibility.
The French company NEXYAD has developed a tool to measure visibility. This tool ( named VisiNex ) is based on a frequency model of human vision ( within the meaning of the angular frequency ) : The human brain needs a different compromise between contrast and luminance depth ( number of bits in a digital image ) , depending on the size of objects . So are we able to detect a star in the night sky ( very small sized, number of luminance levels equal to two ... that is very low ... , very high contrast ) and gray clouds in a gray sky ( very large number of different gray levels that can shape very weak fine gradients, with low contrast) ..


very low contrast (no contour and yet we very high contrast (shapes bounded by an edge)
clearly see the shapes of the clouds). Very poor image grayscale, and high contrast.
rich grayscale.
The comparison between the available contrast (among angular frequency) in the observed scene and the contrast needed to "see", determines the highest detectable angular frequency , which corresponds to the finest level of detail than humans can perceive . This required contrast strongly depends on the size of the objects to be detected , and on global lighting conditions.
Of course, the perceived available contrast also varies depending on the level of ambient light, and other physical parameters ... and also the person (myopia, etc ...)..
For a given object, the highest detectable angular frequency is the maximum distance of the object that still allows to detect it This defines a visibility distance.
Johnson's criteria are used then to determe if the object can be recognized (eg it's a car ) , and identified ( it's this kind of car )
NEXYAD also defines a measure of the " ease " to detect objects , the Visual Quality Score ( VQS ) , defined as the amount of usable available contrast .
The measurement tools of NEXYAD are based on maths models developed and published by the U.S. DoD since the 60s , validated on panels of observers / human watchmen on detection issues of military objects ( tanks, in particular). By construction, the measure 100% correlates with human impression. NEXYAD recently participated in a research program accredited by the French competitive cluster Mov'eo ( SURVIE project, co -funded by French Government/FUI) , with the partners AXIMUM, CETE, IFSTTAR , OKTAL , SAINT GOBAIN , VALEO , and correlation has been validated for road objects (cars, pedestrians, road markings ).
The theoretical principles used by NEXYAD are published ( 70 theses ... ) and NEXYAD also published applications to wipers testing, and also to onboard wipers control ( ITS publication Madrid , 2003) as an alternative to rain sensors (an because the camera is focused on the road THROUGHT the windshield , not ON the windshield, , it allows you to use the camera for other ADAS functions: the camera and NEXYAD software measures visibility among time, and evaluates how wipers has improved - or not - ).
ref :
- On board visibility evaluation for car safety applications : a human vision modelling approach, Gérard Yahiaoui, Pierre Da Silva Dias, conference ITS Madrid, Nov. 2003
- Mesure de Visibilité, final report of the French research program PREDIT / ARCOS 2004, NEXYAD
- Mesure de Visibilité, final report of the French research program PREDIT / SARI 2008, NEXYAD
- Programme de recherche SURVIE (Mov'eo) sur la mesure de visibilité avec VisiNex, poster at Carrefours du PREDIT, 7 & 8 Oct 2013, Paris
The main difficulties of implementing these visibility measurement models are:
- parameters of the human perception maths models and their variations with the physical and physiological cases are only partially published
- the signal to noise ratio heavily depends on the quality of the calibration (which must allow a sensitive, and repeatable "good measurement")
The VisiNex tool developped by the company NEXYAD was used to test the effectiveness of the wiper system (global, or just one part of the wipers system) by equipment manufacturers (references : Robert Bosch GmbH , VALEO ) and car manufacturers (PSA Peugeot Citroen, Toyota ).
http://www.visinex.net/
On the chart below, you can see the visibility climb at every sweep and then visibility decrease again with the rain :
The curves above show the evolution of the VQS (Visual Quality Score) during a watering cycle (artificial rain) with wiping.
The blue curve is obtained with new brushes , red with exhausted brushes.
One can see that the visibility (measured by the VQS ) is maximum before the rain starts. The slope of decrease depends on the type and strength of the rain (the more it rains the less you see , the more drops are thin the more they disturb visibility through the windshield ) . When the rain stops , curves back up to their maximum value and wipers are switched off. Finally, after a dry duration , the rain starts again without wiping (and VQS decreases again).
You understand that such a measurement tool is used to:
- Testing of concurrent systems
- fixing a wiper system and optimizing efficiency
- validating a wiper system
VisiNex is used in different ways ( with different test procedures ) to test point by point and overall a wiper system. The expected values of visibility may be used to write specifications ( click to enlarge ) :
Chart : Use of VisiNex ( visibility measurement ) in the V-cycle
- Design plans #1: on a reference windshield, constant speed wiping with concurrent brushes and with the new blade. Verification of proper restoration of visibility on a set of reference artificial rainfalls
- Design plans #2 : sending reference rains and recording the output of the rain sensor . Along with this record , measurement of visibility with VisiNex and comparison of the two curves : rain sensor output vs. evolution visibility ( the functional purpose as well as is that the rain sensor indirectly captures the reduction in visibility due to rain ) .
- Design plans #3 : sending reference rains and application of wiping strategies. Validation of the restoration of visibility for each rain through the wiping strategy (again , there is much to be gained by adapting the strategy just enough to get the visibility optimization in terms of engine life and power consumption )
- Design plans #4 : sending scenarios of dynamic changes of light and rain ( simulation of a tunnel entrance , a tunnel exit , start a rainstorm , a "truck " rain cloud type , ... ) , the wiper system set to " automatic mode", and recording changes in the visibility among time.
The time saving and performance improvement lead to more competitive solutions.
For more information, please check the NEXYAD web site :
- VisiNex : http://nexyad.net/Automotive-Transportation/?page_id=159


- Rain Machine RainNex : http://nexyad.net/Automotive-Transportation/?page_id=151
- Nexyad Automotive & Transportation : http://www.nexyad.net/Automotive-Transportation
- Nexyad Testing : http://nexyad.net/NonDestructiveTesting/
Contact : sales@nexyad.net







/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F01%2F76%2F1171028%2F90553441_o.png)
/https%3A%2F%2Fassets.over-blog.com%2Ft%2Fcedistic%2Fcamera.png)
/http%3A%2F%2Fstorage.canalblog.com%2F56%2F73%2F1171028%2F108787673_o.jpg)